So, you’re already sold on the benefits of a business process management (BPM) automation solution, and now you just need to know how to develop one for yourself.
Avoid the temptation to just jump in.
Instead, put together a plan from the very beginning so you have a solid idea of where you’re going and how to get there. The following ten steps will give you a broad overview of the BPM implementation strategy we recommend at Nividous.
If at any point you need a more in-depth look at any parts of the process, download our ebook: Business Process Automation: The Step-By-Step Guide.
Or, get started right away and let Nividous handle the technical aspects. Schedule a demo here.
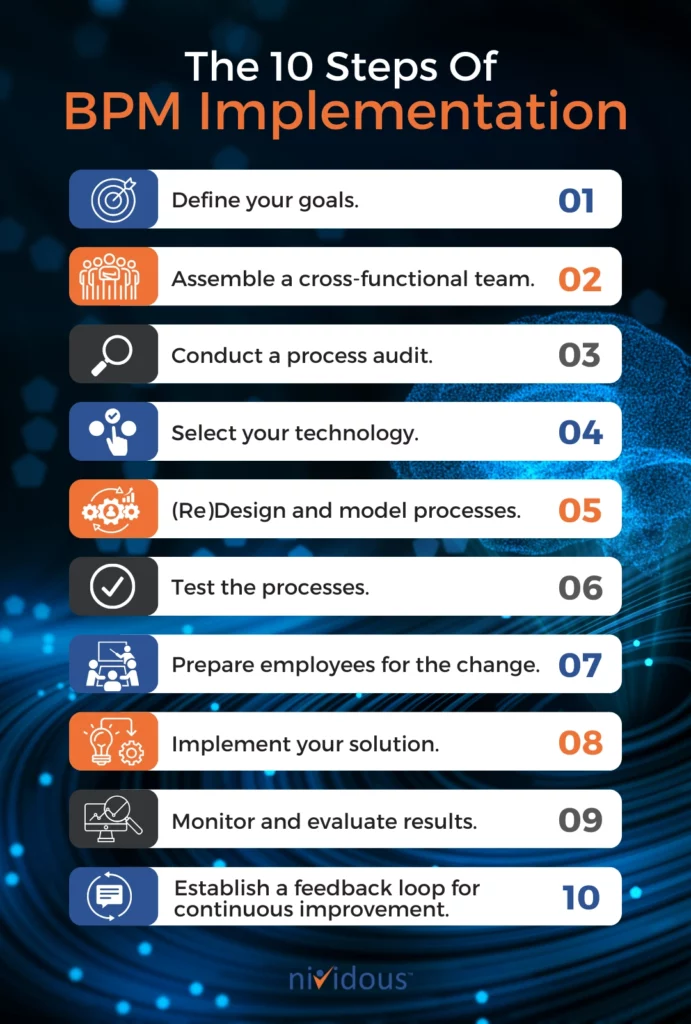
The 10 Steps Of BPM Implementation
1. Define your goals.
What do you want to accomplish from implementing a BPM solution? Are you trying to alleviate a specific pain point? Are you trying to make life easier for your workers, or improve the quality of your customer service?
Whatever your objectives might be, lay them out clearly. They will serve as a guide for the remainder of the implementation process.
2. Assemble a cross-functional team.
Building a custom BPM solution takes more than just a team of technical specialists experienced with AI and programming. You’ll want to have plenty of those folks on your team, of course—or hire experts from a third party, such as Nividous—but you’ll also want stakeholders from key areas of the business present to weigh in on major decisions related to business processes.
Assemble all of your relevant parties into one Center of Excellence—a team that will work together and stay aligned toward your goals throughout the duration of the project.
3. Conduct a process audit.
Before you can automate and streamline your business processes, you must first understand the process landscape across the organization.
Don’t worry if you do not have all of your business processes fully documented, but be sure to include all of the relevant stakeholders in this step so that you don’t miss anything. List each process along with its value to the organization, the approximate number of times each process is completed daily/weekly/monthly, and the average amount of time it takes for completion. This data can form the basis of a value vs. complexity chart that you can use to help identify where the best starting point is.
After that, you can do a deep dive into the relevant process that you want to start with to ensure that you understand all of the people and tools involved in each step as well as where all of the hand-offs occur.
During the process audit, you’ll identify key areas of inefficiency, potential bottlenecks, and any other sticking points that may lead to wasted time, frustrated workers, or slow response times for helping customers.
It’s possible for you to perform a process audit independently, but it can be a cumbersome ordeal. Nividous experts have the software tools and the experience to make this procedure much less tedious.
4. Select your technology.
Selecting the appropriate BPM software or tools is a crucial decision that directly impacts the success of your BPM implementation. The right technology can make the automation and management of your business processes more efficient, while the wrong choice can lead to complications and inefficiencies.
Key Considerations:
- Business Needs Assessment: Begin by conducting a thorough assessment of your organization’s specific needs. Different BPM solutions offer various features and capabilities, so understanding what your business requires is essential.
- Scalability: Consider the scalability of the BPM technology. It should be able to accommodate your organization’s growth and handle increased process complexity.
- Integration Capabilities: Ensure that the chosen BPM software can seamlessly integrate with your existing systems, such as CRM, ERP, or databases. Integration simplifies data exchange and enhances the overall efficiency of your processes.
- User-Friendliness: Evaluate the user-friendliness of the BPM software. It should be intuitive and easy for your team to learn and use. Complicated interfaces can hinder adoption.
- Customization: Look for BPM solutions that allow for customization. Every organization has unique processes, and the software should adapt to your specific requirements.
- Workflow Design: Check if the software offers a robust workflow design interface. Users should be able to create, modify, and optimize process flows without extensive coding.
- Reporting and Analytics: Analytical capabilities are crucial. The BPM software should provide tools for tracking and analyzing process performance, allowing you to identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement.
- Security and Compliance: Ensure that the chosen technology meets security and compliance standards relevant to your industry. Data security and regulatory compliance are non-negotiable.
- Cost and Budget: Consider your budget constraints. Different BPM solutions have varying pricing structures. Evaluate the total cost of ownership over time.
- Vendor Reputation: Research the reputation of the BPM software vendor. Look for customer reviews, case studies, and references. A reliable vendor provides ongoing support and updates.
5. (Re)Design and model processes.
Before you move toward final testing and implementation, you must make sure your solution will do what you want it to do. For example, you might want to model if it will improve the existing business processes to enhance efficiency, reduce errors, and align better with organizational goals. Redesigned processes are better suited for automation, making BPM implementation more effective.
Begin by analyzing your current processes in detail. Identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas where manual interventions are frequent. Then identify and eliminate non-value-adding steps in your processes. These are actions that do not contribute to the end product or customer satisfaction. Streamline the process flow by removing such activities.
Next, identify tasks that are suitable for automation. This includes repetitive, rule-based tasks that can be performed more efficiently by software or machines.
Some things to keep in mind:
- Standardize processes wherever possible. Consistency is key to efficient BPM. Ensure that all team members follow the same procedures to minimize errors and confusion.
- Ensure that the redesigned processes align with the organization’s objectives. Every process should contribute to the achievement of specific goals, whether it’s reducing costs, improving customer service, or increasing efficiency.
- Involve employees who are directly responsible for executing the processes. Their input is invaluable, as they often have practical insights into process challenges and potential improvements.
- Document the redesigned processes thoroughly. Create process maps, flowcharts, or standard operating procedures (SOPs) to clearly illustrate the new workflows. This documentation serves as a reference for all team members.
- Recognize that process redesign can lead to changes in roles and responsibilities. Implement a change management plan to ensure a smooth transition and provide necessary training to employees.
6. Test the processes.
It is essential to conduct thorough testing of the process and automation prior to making any changes to production. For BPM processes, testing is notoriously complex. Making changes in early steps can change the outcomes of subsequent steps. You might make a small change early on and not see the results of that change until twenty steps later.
This means it is incredibly important, though difficult, to automate the testing of BPM solutions. It’s far too easy to run a manual test or two and decide that everything works perfectly, when more thorough tests would have turned up numerous issues that could affect the outcomes.
7. Prepare employees for the change.
Training and change management are essential to a successful BPM implementation. There will always be some resistance to change but manage that by providing good communication and support to your employees throughout the process. Closely monitor engagement and provide channels for feedback and prompt support.
8. Implement your solution.
Once your solution has been built and tested and your employees are prepared for what’s to come, you can officially install it and bring it live.
We’ve found that it’s better to avoid a waterfall style of implementation where everything changes at once. Instead, use an iterative strategy that gives you the ability to keep an eye on the progress and challenges your workers encounter with every new release.
For best results, release your projects in the smallest chunks possible, so you can layer on the changes over time.
9. Monitor and evaluate results.
After your solution is fully in place, try to gauge whether it’s accomplishing your original goals. Find out:
- Does the system deliver the results (ROI) you wanted?
- Has anything fallen through the cracks or gone unaddressed?
- Do your employees know how to work effectively with the new software?
- Is everyone comfortable with the final product?
10. Establish a feedback loop for continuous improvement.
Ideally, you should never stop asking yourself these questions.
Continually checking in on your progress means you can have an ongoing feedback loop telling you whether everything is running optimally, or whether it’s time to make some adjustments. Circumstances will always change over time, so it’s important to keep your eye on progress over the long term.
Fast-forward through the tricky parts by allowing Nividous to build your custom BPM solution.
With our quick start guarantee, we could begin rolling out your project in just three to four weeks.




![Business Process Automation: Your Complete Guide [2023]](https://nividous.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/Business-Process-Automation-Your-Complete-Guide-2023-Blog-Feature.webp)
