Today, businesses striving for growth recognize the importance of intelligent automation technologies in freeing employees to focus on more productive tasks. Among cutting-edge automation technologies, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) have proven their capabilities to significantly reduce operational costs, drive efficiency, enhance customer and employee experiences, and ensure a fast ROI.
However, many businesses need help understanding the distinctions between these two technologies, their unique strengths and applications, and ways to leverage them together for end-to-end automation.
RPA and Artificial Intelligence, while distinct, complement each other seamlessly: RPA handles repetitive, rule-based tasks, while AI enhances processes through data analysis, pattern recognition, and intelligent decision-making. Combining these technologies enables businesses to scale automation efforts, engaging more people in their broader digital transformation goals.
Let’s take a closer look at RPA vs. AI.
What is RPA?
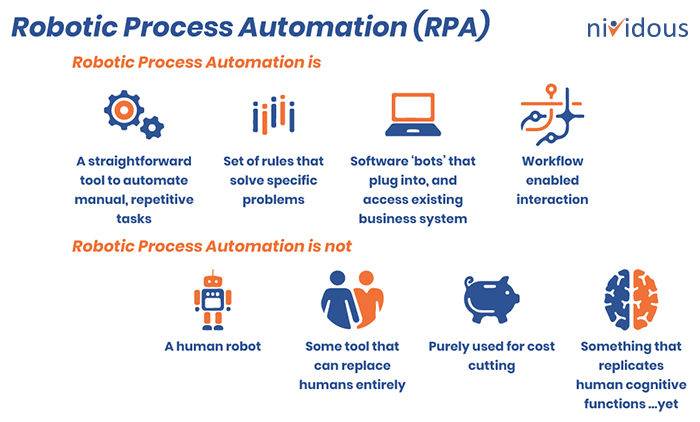
RPA uses software robots (bots) to perform work by emulating human actions through the user interface of any system. These bots are your digital assistants. They let you offload repetitive and arduous tasks that are not complex yet consume valuable employee time.
RPA works best for business processes such as:
- Opening emails and attachments
- Cleaning/formatting Excel sheets
- Navigating different applications/systems to retrieve and insert data
- Extracting data from structured documents
- Performing pre-defined tasks on-demand
- Periodic reporting, data entry, and analysis
The RPA bots can quickly perform tasks the same way every time, without any need for breaks or quality checks. They can also be trained to perform multiple tasks and switch seamlessly from one to another as needed to meet the demand.
Some of the key benefits of using RPA:
- Speed: 4-5 times faster execution with 24/7/365 availability, eliminating delays
- Accuracy: Error-free results minimizing the potential risk and cost
- Compliance: Fully maintained logs (audit trail) essential for appropriate compliance
- Productivity: Freeing up knowledge workers for more value-added tasks
- Efficiency: Integrates scattered processes and systems to deliver enhanced efficiency
Besides, RPA is not just used for cost-cutting. It can improve customer service and boost employee satisfaction, enhancing their engagement and morale.
Read a detailed blog post on the key benefits of RPA here.
RPA is ideal for automating straightforward tasks. However, Artificial Intelligence can take that simple automation to the next level, involving more complex processes that require human-like judgments.
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
AI brings in human-like cognitive decision-making to offload some more manual yet complex work from the human workforce that RPA alone cannot do. AI uses large data sets with quick, iterative processing and intelligent algorithms, allowing the bots to learn from patterns in the data and automate complex processes.
It is essential to learn the key subsets of AI to understand its strengths and use across processes better.
Machine Learning (ML)
ML is an application of AI that focuses on enabling systems to learn and improve from experience without being explicitly programmed. It involves algorithms and statistical models that allow computers to learn patterns from data, make predictions or decisions based on that data, and improve their performance over time through iterations.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP involves enabling computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language. It allows machines to process and analyze large amounts of natural language data, enabling tasks like language translation, sentiment analysis, chatbots, and text summarization.
Computer Vision
This field involves enabling computers to interpret and understand visual information from images or videos. Computer vision algorithms enable tasks such as object recognition, image classification, facial recognition, and image generation.
AI/ML seamlessly augments automation and human experiences by:
- Handling data residing in semi-structured and unstructured documents
- Comprehending conversations using natural language processing
- Discovering processes and tasks for greater automation
- Forecasting with utmost accuracy based on large data sets
AI is a powerful tool that adds human-like intelligence to logic-driven RPA automation. For example, while AI intelligently extracts data from various documents, RPA transcribes the extracted data into any desktop/web-based system in minutes.
What are the examples of RPA and AI applications in the real world?
An Example of RPA for Report Generation
The manual process requires highly valued professionals to generate and distribute several financial reports. Depending on customer requests, they must navigate multiple external websites, legacy systems, and emails.
‘Attended Bots’ with captcha handling capabilities and role-based access easily interact with multiple internal and external investment websites and legacy systems to generate and share various reports. Moreover, automated emails, detailed audit reports, and strict compliance checks can significantly increase the effectiveness of end-to-end automation.
The upshot? Reduced report generation cycle time, improved process visibility, and reduced administrative efforts. Read a detailed blog post on attended vs. unattended RPA automation here.
An Example of Artificial Intelligence for Customer Onboarding
The customer onboarding process generally requires field agents to collect primary details and supportive documents from end customers. Information can be captured on the field with mobile devices and manually verified by back-office staff for further processing.
Besides expediting the verification process, the other primary challenge is detecting fraudulent activities. The risk can be mitigated by deploying AI-enabled automation for intelligent data extraction in the field. This eliminates the post-verification process by administrative staff in addition to minimizing the potential risk of fraudulent activities.
Nividous’ automation platform has native machine learning capabilities that enable accurate detection of text and images from various documents and autofill the data in a mobile app-based application form. Read the complete success story here.

Ready to Transform Your Business with AI, NLP, and Automation?
Watch our on-demand webinar and discover how AI, NLP, and advanced cutting-edge automation technologies can supercharge your growth, streamline processes, and reduce costs.
Understanding key differences between RPA and AI and how they complement each other to deliver greater ROI
Augmented intelligence for complex decision-making
Integrating AI’s cognitive abilities with RPA augments decision-making capabilities within processes. RPA handles routine tasks, while AI makes intricate decisions, ensuring accuracy and adaptability in handling exceptions or unstructured data.
Scalability and adaptability
AI and RPA both scale for complex and more extensive processes, but AI’s edge lies in its adaptability. AI learns and adjusts with data and feedback, handling changes flexibly. RPA may need manual tweaks or programming for new processes, making it less adaptable.
Enhanced customer experience and personalization
AI’s capabilities in natural language processing, sentiment analysis, and predictive modeling enable personalized customer interactions and efficient responses. When combined with RPA, AI can analyze customer data in real-time, allowing RPA bots to tailor interactions or responses according to individual preferences or needs.
Continuous learning and process optimization
Integrating AI into RPA workflows enables the system to learn from RPA-executed tasks, identify patterns, and suggest process optimizations or efficiency improvements. This synergy fosters a continuous improvement cycle, where AI-driven insights refine RPA processes, reducing operational costs, enhancing productivity, and maximizing ROI over time.
Adaptive compliance and risk Management
AI’s ability to analyze large datasets and identify anomalies or risks adds a layer of adaptive compliance and risk management to RPA-driven processes. Real-time risk assessment and compliance monitoring ensure adherence to evolving regulations, minimizing losses due to non-compliance.
When should we deploy RPA, and when should we bring in AI?
A simple rule is to start small by introducing RPA first and then expand the scope of automation leveraging AI.
Start looking for quick wins by analyzing the end-to-end workflow of any process and identify rule-based tasks within that workflow that can be best automated by RPA.
RPA-eligible processes have the following characteristics:
- Repetitive and time-intensive
- Involves high-volume and structured data
- Follows set rules and instructions
- Requires minimal human intervention
- Involves data handling between multiple discrete systems
With RPA, you lay the foundation of an integrated framework on top of your underlying digital systems. Once it is established, it is easier to introduce AI for more complex processes.
The following areas are the ideal candidates for AI-driven automation:
- Processes that require predictive analytics (e.g., inventory forecasts, loan defaults, etc.)
- Processes that are highly variable and do not depend on any set of rules
- Processes that rely on unstructured or semi-structured data
Think about a simple example of invoice automation. Suppose the format of the invoices varies considerably. In that case, Machine Learning (ML) models can be used to train bots to read, interpret, and learn from varied data sets, enabling more accurate invoice processing while improving efficiency.
RPA, AI, and a Holistic Intelligent Automation Strategy with Nividous
Both RPA and AI are here to augment people and not replace them. In other words, automation tackles tasks that can be automated, and employees spend those freed-up man-hours for strategic and cognitive responsibilities. However, human intervention remains crucial for those automated processes for review and decision-making. Human-bot work orchestration is critical in achieving end-to-end process automation, where Nividous stands out.
We advocate for a holistic approach, and our intelligent automation platform is built upon this philosophy. In addition to native RPA and AI capabilities, the platform includes low-code process automation/orchestration, seamlessly uniting processes, departments, and individuals.
This unique approach has empowered numerous customers to achieve their enterprise-wide digital transformation goals while maintaining the lowest total cost of ownership and gaining a distinctive competitive edge. Explore a range of success stories across various industry verticals here.
Are you curious to learn more about the Nividous Intelligent Automation platform?
Discover how the intelligent, flexible, 10X faster Nividous Bots execute real-time error-free automation.
Click any term below to learn more.
Intelligent Automation
The seamless integration of RPA, AI, and workflow automation tools to automate complex, end-to-end business processes for higher efficiency and agility.
RPA (Robotic Process Automation)
Software bots that replicate human actions to perform rule-based, repetitive tasks with speed and accuracy.
Agentic AI
An advanced form of AI that autonomously makes decisions and takes actions to achieve defined goals without human intervention.
Generative AI
AI models, such as ChatGPT and Gemini, that can create original content—text, images, or code—based on natural language prompts.
Low-Code Platform
A visual development environment that enables users to build applications quickly using drag-and-drop components and minimal coding.
Hyperautomation
A strategic approach that leverages multiple technologies—including RPA, AI, and low-code platforms—to automate business processes end-to-end across the enterprise.