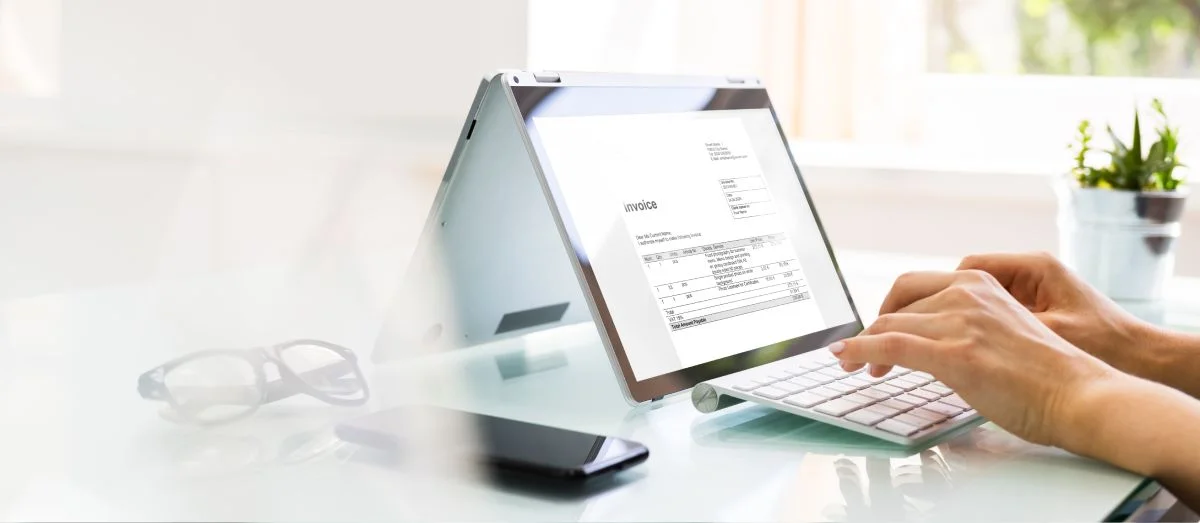
Paying an invoice is more expensive than you might think.
In addition to the invoice price itself, there’s the processing cost—and that varies widely from one Accounts Payable (AP) department to the next. In 2018, the least efficient AP departments spent $10 or more to process an invoice. More streamlined operators spent closer to $2 per invoice, an 80% improvement.
So what’s the difference between the top and the bottom of the AP performers? Often, it is digital infrastructure, including automated invoice processing systems. The fact is, many AP departments overspend on labor—a factor that makes up more than 60% of total AP costs, according to the American Productivity & Quality Center.
Meanwhile, Robotic Process Automation (RPA)—which uses digital “bots” to complete repetitive, data-driven tasks through your existing software systems—can process invoices faster, more accurately, and at a lower cost. Many industries—including banking and financial services—rely on RPA to automate a wide variety of tasks, including invoice processing. This form of automation also frees human staff from necessary but tedious work, allowing them to focus on higher-value operations.
One leading manufacturer automated invoice processing from start to finish with AI-enhanced RPA. They saw powerful benefits, including:
- Invoice processing turnaround time reduced by 90%.
- Over 1,000 staff-hours saved every month.
- Complete elimination of manual errors in invoice processing.

Interested in Taking Your Accounts Payable Functions to The Next Level?
Watch our on-demand webinar and discover how AI-powered intelligent automation helps you accelerate AP efficiency while reducing costs, eliminating manual errors, and optimizing cash flow.
This example isn’t uncommon. According to an Accenture survey, 82% of Chief Financial Officers (CFOs) report measurable returns on investments in digital finance tools like RPA.
But how do RPA bots process invoices? There’s no one-size-fits-all approach; RPA adapts to fit every user’s unique processes. That said, here’s a general model of invoice processing using RPA—and the related technologies that lead to even greater benefits.
Invoice Processing With RPA (And Intelligent Automation)
To understand RPA, start with a close look at the software bot: This isn’t a physical robot, but a digital application that operates existing systems through their user interfaces, almost like a human worker. That makes RPA faster and cheaper to implement than hard-coded software integrations; RPA doesn’t require APIs or programming, so it has a small IT footprint.
To process an invoice, an RPA bot will typically take the following steps:
- Locate invoices. Invoices arrive through many paths. The first step to invoice processing with RPA is to train the bot to retrieve these invoices, whether that’s through a dedicated vendor portal, email accounts, Electronic Data Interchange (EDI), or all of the above.
- Extract relevant data. Once it identifies an invoice, the RPA bot scans it, organizing data to copy it accurately into other applications and systems (like an ERP or accounting software). Data recognition often requires AI components, like computer vision or Natural Language Processing (NLP)—advanced cognitive capabilities that allow bots to identify and sort key data regardless of the invoice format.
- Match invoices to purchase orders and other documentation. Bots compare line items between invoices and related AP documents, like purchase orders or receipts of goods. They validate the information on both ends, and can even send notifications to vendors if they encounter any mismatches.
- Request approval. Bots route invoices to the appropriate manager for approval, and send notifications when payment deadlines approach. They can even process payments following approval (although you may choose to leave this step in human hands). For routine payments, they can even handle the whole process without asking for approvals.
- Posting payments to ERPs. Once the invoice is approved and paid, RPA bots seamlessly post the payments to your ERP—ensuring accurate data and creating a detailed audit log, every step of the way.
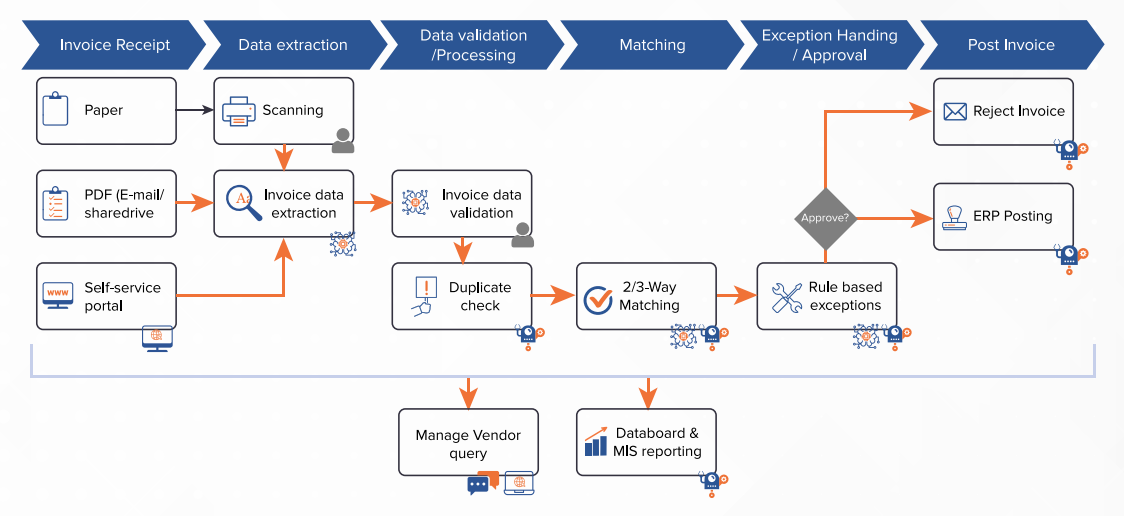
To fully automate invoice processing using RPA, these bots can’t exist in a vacuum. They must fit into broader workflows, which requires an automation platform with a strong core of Business Process Management (BPM). To automate more complex tasks within your invoice processing workflows—and to improve performance over time—bots also need AI components like Machine Learning (ML) and NLP.
The Nividous platform combines all these capabilities into a complete end-to-end automation solution—a higher tier of enterprise technology called intelligent automation, or hyperautomation. While RPA is an important component in end-to-end business process automation, BPM and AI are also crucial if you want to fully automate invoice processing. Doing so could revolutionize your AP department, with wide-ranging benefits from lower costs to better regulatory compliance.
Ready to learn more?
Schedule a free, personalized demo to see how invoice processing using RPA can help your organization.





